Grasping the basics of product identification and stock-keeping units is crucial for businesses. Product identification involves assigning unique codes or names to products to distinguish them from one another. On the other hand, SKUs are alphanumeric codes used to track inventory and sales. By using SKUs, businesses can efficiently manage their stock and improve the accuracy of their inventory records.
This is essential for smooth operations and customer satisfaction. Additionally, SKUs can provide valuable data for analyzing sales trends and making informed business decisions. In this article, we will perceive into the significance of product identification and SKUs, investigating their role in streamlining business processes and enhancing overall efficiency.

| Table of Content |
What is SKU?
A Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) is a unique code used by retailers and warehouses to identify and track inventory. SKUs are key for managing stock levels, simplifying the ordering process, and raising the shopping experience bar, both in-store and online. Each SKU is linked to specific product details, such as color, size, brand, and style, making it easier for businesses to monitor their products.

For example, an SKU might be “SHOE123BLK9” for a size nine black shoe of a particular brand. Unlike Universal Product Codes (UPCs), which are the same for a product regardless of where it’s sold, SKUs are unique to each store or company. This system allows for more detailed inventory management, helping businesses to quickly identify items that need restocking and analyze sales patterns.
SKU number Example
In today’s retail environment, tracking product information is a hack to achieve more outstanding goods. SKU numbers, barcodes, and UPC numbers immensely influence inventory management and sales tracking. By grasping how SKU numbers and barcodes function, businesses can streamline their processes and raise their overall performance.
– SKU Number
A Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) is a code made up of letters and numbers that is used by retailers to keep track of their products. Each product has its own unique SKU, which helps the retailer manage inventory and sales. The SKU can contain details about the product, like the brand, size, color, and category.
For instance, a red t-shirt from brand ABC in size large might have an SKU like “RDABC-LRG.” The SKU system makes it easier for retailers to organize and find products in their inventory.
– Barcode
A barcode is a visual representation of data that optical readers can scan. It consists of black-and-white lines or patterns representing numbers or other symbols. Barcodes are used to quickly convey product information, such as price or inventory level, at the point of sale.
They can be one-dimensional (1D), consisting of lines, or two-dimensional (2D), such as QR codes, containing more complex information. Barcodes help businesses keep track of inventory and sales, and they make the checkout process faster and more accurate. Additionally, they are used in various industries to track and manage items, from retail to healthcare and logistics.
– UPC Number
The Universal Product Code (UPC) is a specific type of barcode that is widely used in retail. It consists of a 12-digit number that uniquely identifies a product and its manufacturer. This UPC is encoded within the barcode and is scanned at the point of sale to retrieve the product’s information, including its price and inventory status.
Each UPC is unique to a product, making it a global standard for tracking trade items. This system helps in efficient inventory management and enables accurate and speedy checkout processes. Additionally, it provides valuable data for manufacturers and retailers to track sales and stock levels.
Why is SKU Important?
Why are SKU numbers significant? SKU numbers help businesses keep track of inventory and easily identify products. Businesses can efficiently manage stock, track sales, and analyze product performance by using unique SKU numbers.

– Inventory Tracking
SKUs are individual codes assigned to products for precise inventory tracking. These codes enable businesses to monitor stock levels accurately, facilitating efficient inventory management. Along with SKUs, companies can oversee stock availability, streamline reordering procedures, and prevent both excess inventory and stock shortages. By benefiting from SKUs, businesses guarantee that products are consistently available for customers, raising customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
– Sales Analysis
SKUs play a crucial role in sales analysis by providing valuable insights into sales trends and customer preferences. By analyzing SKU data, companies can understand which products are selling well, identify popular items, and make informed decisions about product offerings and promotions. This data-driven approach helps businesses optimize their product mix and tailor their marketing strategies to meet customer demands.
– Operational Efficiency
SKUs create a roadway to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction across various business processes that lead to success. Tasks such as order fulfillment, warehousing, and checkout procedures can be accomplished by compacting and expediting these operations. SKUs enable firms to easily and flawlessly identify and locate products, facilitating faster order fulfillment while minimizing errors.
This efficiency accelerates the delivery process and improves the overall customer experience. Customers benefit from quicker transactions and accurate order processing, which increases satisfaction with the service provided. Moreover, businesses can optimize their inventory management practices, reduce costs, and increase profitability by leveraging SKUs effectively. Integrating SKUs into operational workflows significantly contributes to smoother processes, heightened efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction in retail and logistics operations.
SKU vs UPC
SKU and UPC are different types of codes used to identify products.

SKU (Stock Keeping Unit)
- SKUs, also known as stock-keeping units, do individual retailers use alphanumeric codes for tracking their inventory. These codes help retailers manage and organize their products efficiently.
- Retailers have the flexibility to create their SKUs, allowing for customization in terms of length and format. Typically, these codes range from 8 to 12 characters, providing a unique identifier for each product.
- It’s important to note that each retailer has its own set of SKUs. As a result, the same product can have different SKUs in different stores. This allows retailers to best adapt their inventory systems to suit their specific needs and processes.
UPC (Universal Product Code)
- Universal Product Codes (UPCs) are numeric codes used by various retailers for external purposes such as scanning at the point of sale. This enables efficient inventory management and tracking of sales.
- UPCs consist of 12 digits, ensuring a standardized format that is consistent across all retailers. This standardization simplifies the process of product identification and enhances accuracy in retail operations.
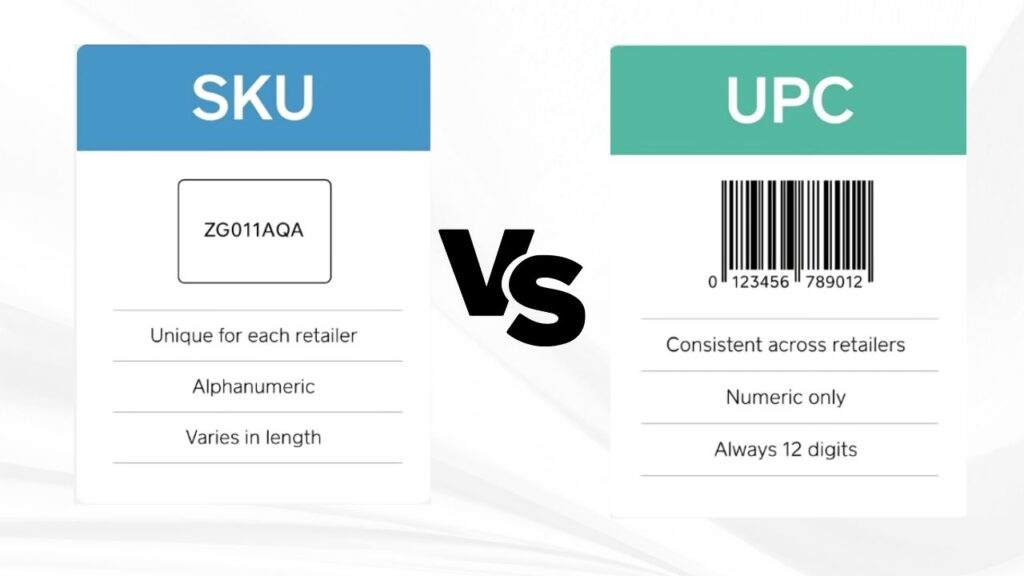
- A product’s UPC remains the same regardless of the retailer selling it, establishing a global standard for product identification. This global standardization facilitates seamless product tracking and ensures clarity and consistency in product information across different retail platforms.
FAQs about SKU
1. Where is the SKU on a product?
The Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) is a code usually seen on a product’s packaging near the barcode. It can also appear on the price tag, either attached to the item or displayed on the shelf. Sometimes, the SKU might be sewn into the product or on a sticker, especially with clothing and toys. The SKU is crucial for retailers to manage their inventory and sales effectively. While customers may see it, its main purpose is for an internal inventory system.
2. How to create SKU numbers?
Creating SKU numbers follows a systematic process to make them easy to understand and manage:
- Know the key features that set your products apart, such as category or brand.
- Create a consistent structure for all SKUs, typically using a mix of letters and numbers to represent various product attributes.
- Begin the SKU with the primary characteristic, like category or manufacturer.
- Use the middle part of the SKU for unique details like size, color, or style.
- Finish the SKU with a sequential number to distinguish items with the same attributes.
- Make sure the SKU is concise for easy readability and efficient inventory management.
Conclusion
Product identification and SKUs play a great part in effective inventory management and retail operations. SKUs serve as unique product identifiers, enabling businesses to track inventory levels accurately, manage reordering processes efficiently, and prevent stock-related issues such as overstocking or stockouts.
Using a systematic approach to creating SKUs based on key product characteristics, companies can bulk up their inventory management workflows and make sure that products are consistently available for customers. But if you are looking for a feasible way to ship things, NextSmartShip is an ideal option. It offers the best shipping rates for both standard and express shipping options, making it an optimal choice for efficient and cost-effective order fulfillment.



